In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, staying ahead of the curve requires more than just traditional methods. Modern enterprises are turning to sophisticated solutions like Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) to streamline operations, enhance efficiency, and drive growth. But what exactly is ERP, and how does it work within organizations? Let’s delve into the intricacies of ERP to understand its significance and functionality.
What is Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP)?
At its core, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a robust software solution designed to integrate and streamline core business processes across various departments within an organization. This comprehensive system acts as a centralized hub, enabling seamless communication and data sharing between different functions, such as finance, supply chain management, human resources, and customer relationship management.
Why is ERP Important for Businesses?
- Streamlining Operations: ERP automates routine tasks and workflows, reducing manual effort and eliminating redundancies. By providing a single source of truth for data, ERP enhances efficiency and productivity across the organization.
- Improving Decision-Making: With real-time access to key performance metrics and analytics, ERP empowers decision-makers to make informed choices. By leveraging actionable insights, businesses can adapt quickly to changing market dynamics and stay ahead of the competition.
Key Components of ERP
- Financial Management: ERP systems include modules for accounting, budgeting, and financial reporting. These tools help organizations track and manage their finances effectively, ensuring compliance and transparency.
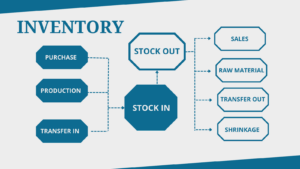
- Supply Chain Management: ERP streamlines procurement, inventory management, and logistics operations. By optimizing the supply chain, businesses can reduce costs, minimize stockouts, and improve customer satisfaction.
- Human Resource Management: From employee data management to payroll processing, ERP simplifies HR tasks and enhances workforce management. By automating routine HR processes, businesses can focus on talent development and employee engagement.
How Does ERP Benefit Different Departments?
- Human Resources: ERP facilitates employee data management, performance tracking, and training administration. HR departments can use ERP to streamline recruitment, onboarding, and talent management processes.
- Sales and Marketing: ERP systems often include Customer Relationship Management (CRM) modules, allowing businesses to track leads, manage customer interactions, and analyze sales performance. By aligning sales and marketing efforts, organizations can drive revenue growth and foster customer loyalty.
Steps Involved in Implementing ERP
- Planning Phase: Define project objectives, assess business requirements, and select an ERP system that aligns with organizational goals.
- Execution Phase: Configure and customize the ERP system to meet specific business needs, migrate data from legacy systems, and provide training to end-users.
- Monitoring and Optimization: Continuously monitor ERP performance, gather feedback from users, and make adjustments as needed to optimize system efficiency and effectiveness.
Maximizing the Value of ERP
- Training and Adoption: Invest in comprehensive training programs to ensure that employees are proficient in using the ERP system. Encourage adoption by highlighting the benefits of ERP and providing ongoing support.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly review and update ERP processes to keep pace with evolving business requirements and industry trends. Leverage ERP analytics to identify areas for improvement and drive continuous innovation.
In conclusion, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) is a powerful tool that empowers businesses to streamline operations, enhance decision-making, and drive growth. By embracing ERP and leveraging its capabilities, organizations can unlock new opportunities for success in today’s competitive marketplace.